The first step to solving a problem is to define the problem precisely. It is the heart of problem-solving.
Root cause analysis is the second important element of problem-solving in quality management. The reason is if you don't know what the problem is, you can never solve the exact problem that is hurting the quality.

Manufacturers have a variety of problem-solving tools at hand. However, they need to know when to use which tool in a manner that is appropriate for the situation. In this article, we discuss 7 tools including:
- The Ishikawa Fishbone Diagram (IFD)
- Pareto Chart
- 5 Whys
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Scatter Diagram
- Affinity Diagram
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
1. The Ishikawa Fishbone Diagram IFD
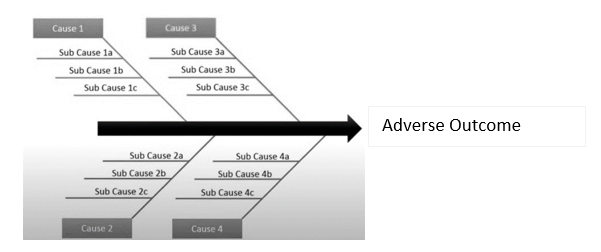
The model introduced by Ishikawa (also known as the fishbone diagram) is considered one of the most robust methods for conducting root cause analysis. This model uses the assessment of the 6Ms as a methodology for identifying the true or most probable root cause to determine corrective and preventive actions. The 6Ms include:
- Man
- Machine
- Methods
- Materials
- Measurement,
- Mother Nature- i.e., Environment
Related Training: Fishbone Diagramming
2. Pareto Chart
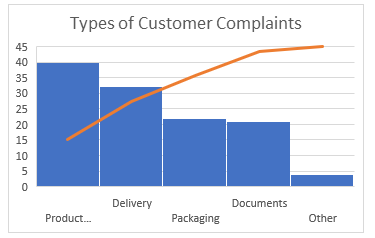
The Pareto Chart is a series of bars whose heights reflect the frequency or impact of problems. On the Chart, bars are arranged in descending order of height from left to right, which means the categories represented by the tall bars on the left are relatively more frequent than those on the right.
Related Training: EFFECTIVE INVESTIGATIONS AND CORRECTIVE ACTIONS (CAPA) Establishing and resolving the root causes of deviations, problems and failures
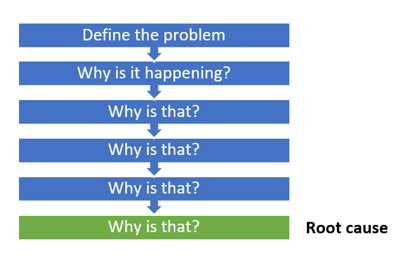
3. 5 Whys
This model uses the 5 Why by asking why 5 times to find the root cause of the problem. It generally takes five iterations of the questioning process to arrive at the root cause of the problem and that's why this model got its name as 5 Whys. But it is perfectly fine for a facilitator to ask less or more questions depending on the needs.
Related training: Accident/Incident Investigation and Root Cause Analysis
4. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
| Process |
Failure |
Effect |
S |
Causes |
O |
D |
RPN |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FMEA is a technique used to identify process and product problems before they occur. It focuses on how and when a system will fail, not if it will fail. In this model, each failure mode is assessed for:
- Severity (S)
- Occurrence (O)
- Detection (D)
A combination of the three scores produces a risk priority number (RPN). The RPN is then provided a ranking system to prioritize which problem must gain more attention first.
Related Training: Failure Mode Effects Analysis
5. Scatter Diagram
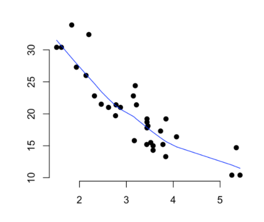
A scatter diagram also known as a scatter plot is a graph in which the values of two variables are plotted along two axes, the pattern of the resulting points revealing any correlation present.
To use scatter plots in root cause analysis, an independent variable or suspected cause is plotted on the x-axis and the dependent variable (the effect) is plotted on the y-axis. If the pattern reflects a clear curve or line, it means they are correlated. If required, more sophisticated correlation analyses can be continued.
Related Training: Excel Charting Basics - Produce Professional-Looking Excel Charts
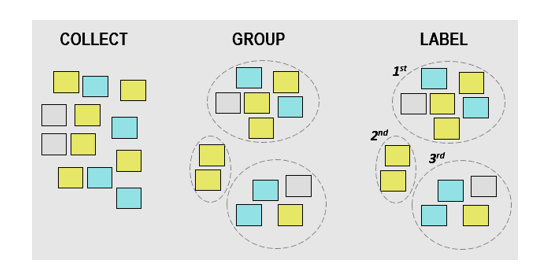
6. Affinity Diagram
Also known as KJ Diagram, this model is used to represent the structure of big and complex factors that impact a problem or a situation. It divides these factors into small classifications according to their similarity to assist in identifying the major causes of the problem.
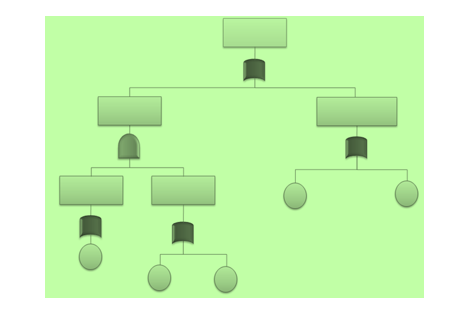
7. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
The Fault Tree Analysis uses Boolean logic to arrive at the cause of a problem. It begins with a defined problem and works backward to identify what factors contributed to the problem using a graphical representation called the Fault Tree. It takes a top-down approach starting with the problem and evaluating the factors that caused the problem.
Finding the root cause isn't an easy because there is not always one root cause. You may have to repeat your experiment several times to arrive at it to eliminate the encountered problem. Using a scientific approach to solving problem works. So, its important to learn the several problem-solving tools and techniques at your fingertips so you can use the ones appropriate for different situations.
ComplianceOnline Trainings on Root Cause Analysis
P&PC, SPC/6Sigma, Failure Investigation, Root Cause Analysis, PDCA, DMAIC, A3
This webinar will define what are the US FDA's expectation for Production and Process Control / Product Realization, the use of statistical tehniques, 6 sigma, SPC, for establishing, controlling , and verifying the acceptability of process capability and product characteristics, product acceptance or validation and other studies. Non-conformance, OOS, deviations Failure Investigations, and Root Cause Analysis, PDCA, DMAIC, and similar project drivers to improvement, A# and similar dash boards.
Accident/Incident Investigation and Root Cause Analysis
If a major workplace injury or illness occurred, what would you do? How would you properly investigate it? What could be done to prevent it from happening again? A properly executed accident/incident investigation drives to the root causes of the workplace accident to prevent a repeat occurrence. A good accident/incident investigation process includes identifying the investigation team, establishing/reviewing written procedures, identifying root causes and tracking of all safety hazards found to completion.
Root Cause Analysis - The Heart of Corrective Action
This presentation will explain the importance of root cause analysis and how it fits into an effective corrective and preventive action system. It will cover where else in your quality management system root cause analysis can be used and will give examples of some of the techniques for doing an effective root cause analysis. Attendees will learn how root cause analysis can be used in process control.
Addressing Non-Conformances using Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
RCA assumes that systems and events are interrelated. An action in one area triggers an action in another, and another, and so on. By tracing back these actions, you can discover where the issue started and how it grew into the problem you're now facing.
Risk Management Under ISO 14971
ISO 14971:2019 is the definitive standard for risk management for medical devices and IVDs. The standard lays out a comprehensive approach to managing risks in the life sciences. The course will discuss practical approaches to complying with the standard.
Introduction to Root Cause Investigation for CAPA
If you have reoccurring problems showing up in your quality systems, your CAPA system is not effective and you have not performed an in-depth root cause analysis to be able to detect through proper problem solving tools and quality data sources, the true root cause of your problem. Unless you can get to the true root cause of a failure, nonconformity, defect or other undesirable situation, your CAPA system will not be successful.
Root Cause Analysis and CAPA Controls for a Compliant Quality System
In this CAPA webinar, learn various regulations governing Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) and how organization should collect information, analyze information, identify, investigate product and quality problems, and take appropriate and effective corrective and/or preventive action to prevent their recurrence.
How to Design and Implement a Dynamic Control Plan
This webinar training will discuss how to design a dynamic control plan that combines FMEA and the control plan by extending the FMEA to encompass the elements of the control plan and create a living document that helps to drive continual improvement.
An Easy to Implement Integrated Risk Management Approach Compliant with ISO 14971
This integrated risk management training for medical devices will discuss how to incorporate risk management as per ISO 14971 guidelines in all phases of medical device development. It will highlight the documentation needed to support the decisions made as part of the risk management process.
The Use and Mis-use of FMEA in Medical Device Risk Management
The presentation will discuss the proper use of FMEA in risk management and how to recognize and avoid the traps associated with this tool in order to have a more efficient risk management process. Most medical device manufacturers use FMEA as a part of their risk management system. Most medical device manufacturers use FMEA as a part of their risk management system.
Root Cause Analysis for CAPA Management (Shutting Down the Alligator Farm)
Emphasis will be placed on realizing system interactions and cultural environment that often lies at the root of the problem and prevents true root cause analysis. This webinar will benefit any organization that wants to improve the effectiveness of their CAPA and failure investigation processes.
Root Cause Analysis for Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
The Quality Systems Regulation (21 CFR 820) and the Quality Management Standard for Medical Devices (ISO 13485:2003), require medical device companies to establish and maintain procedures for implementing corrective and preventive action (CAPA) as an integral part of the quality system.
Strategies for an Effective Root Cause Analysis and CAPA Program
This webinar will provide valuable assistance to all regulated companies, a CAPA program is a requirement across the Medical Device, Diagnostic, Pharmaceutical, and Biologics fields. This session will discuss the importance, requirements, and elements of a root cause-based CAPA program, as well as detailing the most effective ways to determine root cause and describing the uses of CAPA data.
Legal Disclaimer
This piece of content and any of its enclosures, attachments or appendices, references are created to provide solely for information purpose. ComplianceOnline has made all effort to provide accurate information concerning the subject matter covered. This content is created from interpretation, and understanding of relevant and applicable information and it is not all inclusive. It can be best used in conjunction with your professional judgment and discretion.
However, this piece of content and any other ancillary items disseminated in connection with same are not necessarily prepared by a person licensed to practice law in a particular jurisdiction. This piece of content is not a substitute for the advice of an attorney. If you require legal or other expert advice, you should seek the services of a competent attorney or other professional.
ComplianceOnline necessarily is not, cannot and will not be liable for any claims, damages, or regulatory legal proceedings initiated as a consequence of you using whole or any part of the content present in this document. If any action, claim for damages, or regulatory proceedings is commenced against ComplianceOnline as a consequence of your use of this document, then and in that event, you agree to indemnify ComplianceOnline for such claims, and for any attorney's fees expended by ComplianceOnline in connection with defense of same.













