Quality Control Laboratory Compliance - Documentation and Record-Keeping explained
Paper and electronic laboratory documents are a crucial part of your daily operations. It is important to manage them well with a good system. This article is designed to help you gain an understanding of proper documentation and record-keeping for the successful performance.

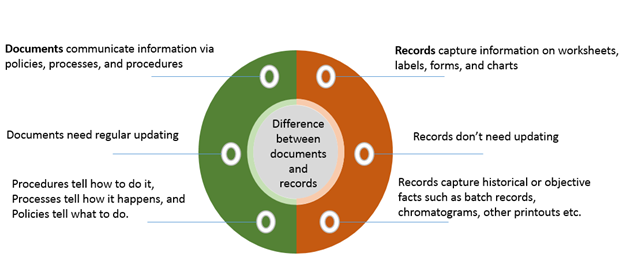
The difference between documentation and records
The importance of laboratory documents
Documents provide essential guidelines for the laboratory in the form of a quality manual, SOPs and reference material. They are required part of the laboratory quality standards. They reflect the laboratory's organization and quality management. Laboratories maintain documents and records to find information when it is needed. Verbal instructions often go unheard, or are misunderstood, quickly forgotten, or difficult to follow.
To examine the fundamental requirements for all QC laboratories subject to FDA inspection, recent trends from FDA inspection reports and enforcement actions, attend the seminar Quality Control Laboratory Compliance - cGMPs and GLPs.
The importance of laboratory records
Records are management tools that help in the continuous management of the quality system. They also help track samples throughout the process and identify problems. They indicate how your staff has been operating. Poor record keeping is often an indication of poor performance and disorganization. Records help in decision making.
Laboratory documents
Important laboratory documents include the Quality manual, SOPs, controlled documents, personnel files, Instrument files, equipment maintenance, calibration and verification, quality control, temperature and humidity logs, test tracking system, proficiency testing, and quality assessment. They are briefly outlined below:
- Quality manual
- It is a roadmap for meeting the quality systems requirement
- It is an indication of the management's commitment to quality
- There should be only one official version of Quality control manual
- Should be improved on an ongoing basis
- Should be read and accepted by everyone
- Should be in clear language
- Should provide uniformity in testing over time, and from one person to the next
- Outline of a quality manual
- Introduction
- Organization and management
- Quality policy 4. Personnel (staff education and training )
- Document control, including records, maintenance and archiving
- Accommodation and environment
- Instruments, reagents, consumables management
- Safety
- Research and development (optional)
- Pre-examination procedures
- Examination procedures
- Post-examination procedures
- Quality control
- Laboratory information system
- Handling of complaints - occurrence management
- Communications and other interactions
- Preventive and corrective action, internal audit
- Ethics
- SOPs
- Should contain step by step instructions on how to perform a test
- Should be consistent, accurate and of high quality
- Should be easily understood by new staff
- Should be reviewed and approved by management
- Should be updated regularly
- Should not drown the details
- SOP for Routine inspection, cleaning, maintenance, testing, and calibration.
- Controlled documents
- SOPs, texts, articles, reference books, equipment service manuals, regulations, and standards
- Have a system in place for organizing, approval, and revision
- Maintain a master log that describes the documents in circulation
- Should be accessible at the point of use
- Should have an archiving system
- Personnel files
- education, experience, training, and continuing education
- Instrument Files
- Instrument name
- The model number and serial number
- Purchase date
- Manufacturer and/or supplier contact information
- Technical service contact information
- Repair service contact information
- Warranty information
- Preventive maintenance and repair services performed by company representatives
- Verification of performance specifications, if applicable
- Equipment Maintenance
- SOPs
- Maintenance logs
- Calibration and Calibration Verification
- Quality Control (QC)
- quality control results
- Graph quantitative results for visual evaluation of shifts and trends over time
- Recognized problems and corrective actions to address them
- Temperature and Humidity Logs
- Must be monitored and recorded daily
- Test Tracking System
- Test requisitions
- Testing records
- Test reports
- Proficiency Testing (PT)
- A copy of the PT enrollment order form
- The instructions that come with the samples
- All worksheets and instrument printouts of testing
- A copy of the final completed result form that you send to the PT provider, including the signed attestation statement
- The reviewed PT score report, including the CMS summary page
- Documentation of investigations and corrective actions for any PT failure
- Quality Assessment (QA)
Laboratory records that should be kept
Section 211.67(c)- maintenance, cleaning, sanitizing, and inspection as specified in B'B' 211.180 and 211.182.
Section 211.68(a)- calibration checks, inspections, and computer or related system programs for automatic, mechanical, and electronic equipment.
Section 211.68(b)- All appropriate controls must be exercised over all computers or related systems and control data systems to assure that changes in master production and control records or other records are instituted only by authorized persons.
Section 211.105(b)-Major equipment must be identified by a distinctive identification number or code that must be recorded in the batch production record to show the specific equipment used in the manufacture of each batch of a drug product.
Section 211.160(a) - The establishment of any specifications, standards, sampling plans, test procedures, or other laboratory control mechanisms, including any change in such specifications, standards, sampling plans, test procedures, or other laboratory control mechanisms, must be drafted by the appropriate organizational unit and reviewed and approved by the quality control unit. These requirements must be followed and documented at the time of performance. Any deviation from the written specifications, standards, sampling plans, test procedures, or other laboratory control mechanisms must be recorded and justified.
Section 211.194-Describes laboratory records that must be retained.
Section 211.182-Specifies requirements for equipment cleaning records and the use log.
Current Good Laboratory Practices (cGLPs)
21 CFR Part 58) - Good laboratory practice for nonclinical laboratory studies
40 CFR Part 160 FIFRA - Protection of environment, Good laboratory practice standards
Regulations and statutes - records retention and document controls
21 CFR Part 11 Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures
(the European version of this regulation is Annex 11).
Part 11 FAQ on retention of paper versus electronic records
- Electronic-records/signatures must be equivalent to paper records/sigs
- Procedures and controls must include:
- Systems validation
- Protection of records throughout the retention period
- Limited systems access
- Time-stamped audit trails
- Systems, Authority, and Device checks
- Personnel who have adequate training & experience
- Control over system documentation
Documentation best practices, storage and retention
- Whether electronic or paper, documents must be clear, concise, user-friendly, explicit, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Draft documents must be compliant with established standards
- Update documents and maintain records regularly
- Use the most current version
- Document preparation and control process includes the following in sequence
- Prepare
- Review
- Revise
- Approve
- Distribute
- Retain things you might forget
- Documents should permit the complete reconstruction of a study
- Properly head all pages, tables, columns; identify units Properly head all pages, tables, columns; identify units Describe Statistical & Calculation Procedures used Describe Statistical & Calculation Procedures used Sign, Date, and File automated printouts
- Store documents in an orderly manner
- Laboratory director, the laboratory consultant, inspectors, and accreditation agency surveyors should be able to promptly retrieve documents
- Ensure that all documentation is maintained for the proper length of time.
- Most documents and records generated in the laboratory must be available for two years
- Some must be stored for a longer time period
Storage
Attend the seminar Quality Control Laboratory Compliance - cGMPs and GLPs to examine the fundamental requirements for all QC laboratories subject to FDA inspection, recent trends from FDA inspection reports and enforcement actions.
Ms. Thomas has over two decades of cGMP hands-on industry experience in both pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing operations. Her experience covers all Quality Systems; as well as, all areas of validation; including, process/product validation, facilities validation, CSV and 21 CFR Part 11, test method validation, equipment/automated processes and cleaning validation. Utilizing strategic thinking, risk-based approaches, and Lean principles, she has demonstrated success in steering and managing complex projects within the pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
FAQs on Quality Control Laboratory Compliance
What’s the difference between laboratory “documents” and “records” — and why does it matter?
Documents are the instructions, SOPs, quality manuals and policies that tell your lab how things should be done; records are the evidence of what was done — test results, logs, maintenance entries. According to the article, documents help ensure consistency and quality over time, while records act as management tools, showing how your team actually worked, helping track samples, identify problems and support decisions.
Understanding this difference matters because many compliance and inspection issues stem from poor record-keeping (e.g., missing logs) even when documents exist.
2. What key documents should a QC laboratory keep under control?
Some of the essential documents listed include: the quality manual (as a roadmap for your quality system), SOPs (for each routine inspection/maintenance/test), instrument files (model, serial no., service history), personnel files (training, qualification), calibration logs, temperature/humidity logs, test tracking systems and proficiency testing records.
In short: any document that supports your laboratory’s structure, steps, equipment and personnel must be controlled, versioned, approved and available at the point of use.
3. How long should we retain laboratory records, and what about electronic vs paper?
The article explains that for laboratories under regulatory oversight (e.g., under 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records), retention requirements apply both to paper and electronic formats. Documents should permit the reconstruction of a study or test. For example, historical logs must be readily retrievable and protected for the appropriate duration.
While it doesn’t give one universal number (because it depends on the jurisdiction/product type), the principle is: store records long enough to reconstruct the test/process, protect integrity, and follow your regulatory/contractual obligations.
4. What are the best practices for document control in the lab?
Key practices include: preparing the document, reviewing it, revising it, approving it, distributing it. After this, it must be used and archived properly.
Other best practices: give each document a unique ID and version number, ensure only the latest approved version is in use, archive obsolete versions, ensure documents are readable, clear and user-friendly, and accessible at the point of use. All these steps help avoid regulatory observations about outdated or uncontrolled documents.
5. Why are electronic records and signatures becoming so important, and what should a laboratory consider?
Electronic records and e-signatures are subject to the same principles of integrity and traceability as paper records. The article highlights that systems must be validated, have audit trails, restricted access, and ensure changes can only be made by authorized persons.
Laboratories should consider: is the system validated for its intended use? Does it log who did what and when? Can you retrieve and review changes? Are original raw data traceable? These are critical to meet requirements like 21 CFR Part 11 and similar.
6. What common inspection or compliance risks do QC laboratories face in documentation and records?
Some risks include missing raw data, inconsistent or uncontrolled document versions, lack of audit trails on electronic systems, incomplete or illegible records, and inability to trace changes or reconstruct a test.
By keeping your documents and records well-organized, accessible and under control, you reduce risks of regulatory findings, and improve your lab’s readiness for audits and inspections.






