From the Manufacturer to the Patient - Transportation Studies to Minimize Temperature Excursions
Pharmaceutical products that are "temperature sensitive" require to be stored within the designated temperature range to ensure that product quality, safety, efficacy, and stability is maintained. Throughout its life-cycle from the manufacturing site, during transit, at warehouse, clinic or a retail outlet, it is the manufacture's responsibility to ensure that the patient receives it in safe, effective, and of acceptable quality.

With the rapid growth of biopharmaceuticals, global sourcing and distribution requires the use of complex distribution chains with a variety of transportation modes. This calls for an effective transportation study to minimize temperature excursions. Before diving into the transportation study, it is important to understand the associated preliminary information.
Cold chain or cold chain management
The transportation of pharmaceutical products, biologicals, and active ingredients in controlled temperature is in short known as cold chain or cold chain management. Cold chain applies to
- Diagnostics, research, and investigational materials that require temperature control
- Any pharmaceutical product, biological, active ingredient, devices, and combination products
- Animal products
- Finished products such as labeled products, unlabeled bulk products, finished products
- Process intermediates
- Reference standards
- Samples (for GMP testing)
While maintaining the stability of the product, an effective cold chain management minimizes the cost, increases efficiency and helps in complying with the regulatory requirements.
Regulatory references
- ICH Q1(R2) - Section 2.2.7 Storage Conditions
'A drug substance should be evaluated under storage conditions (with appropriate tolerances) that test its thermal stability and, if applicable, its sensitivity to moisture. The storage conditions and the lengths of studies chosen should be sufficient to cover storage, shipment, and subsequent use.'
'Data from the accelerated storage condition and, if appropriate, from the intermediate storage condition can be used to evaluate the effect of short term excursions outside the label storage conditions (such as might occur during shipping).' - FDA, CFR 21 Part 203.32
'Storage and handling conditions. Manufacturers, authorized distributors of record, and their representatives shall store and handle all drug samples under conditions that will maintain their stability, integrity, and effectiveness and ensure that the drug samples are free of contamination, deterioration, and adulteration.' - FDA, 21 CFR 211.150 - Procedures for distributors
- FDA, 21 CFR 203 and 205 - Good practices for holding procedures
- EU Guidance (94/C63/03)
Distributors (wholesalers) of medicinal products are required to maintain quality systems that ensure Storage conditions to be observed at all times, including during transportation
Transportation Studies
The manufacturer is expected to have a thorough understanding of the product's stability and have the required controls during the distribution process. This can be achieved only if the manufacturer understands every aspect of the distribution chain including responsibilities of manufacturer, shipper and receiver.
The Prerequisites
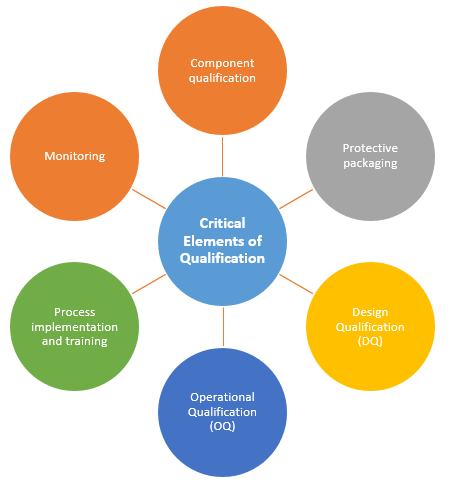
Critical Elements of Qualification
Why Stability Studies are important
- 'The purpose of stability testing is to provide evidence on how the quality of a drug substance or drug product varies with time under the influence of a variety of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, and to establish a retest period for the drug substance or a shelf life for the drug product and recommended storage conditions.' ICH Q1A (R2)
- 'In general, a drug substance should be evaluated under storage conditions (with appropriate tolerances) that test its thermal stability and, if applicable, its sensitivity to moisture. The storage conditions and the lengths of studies chosen should be sufficient to cover storage, shipment, and subsequent use.' ICH Q1A (R2)
- Storage and transport stability data should be generated, showing the effect of exposure to extremes of temperature, vibration, etc. on the drug product.
- Helps identify the degradation of a product
- Helps identify failure points for a product
- Combining stability data from long-term and accelerated studies, temperature excursion studies, and temperature cycling studies will provide information needed to evaluate the effect of temperature excursions on drug product quality that may occur during the storage and transportation process.
- Stability testing permits the establishment of recommended storage conditions, retest periods, and shelf-lives.
- How a product-related factor influences the quality of the product is also included in a stability program. Example: The interaction of API with excipients, container closure systems and packaging materials.
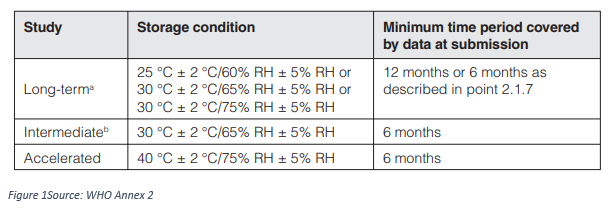
- Storage Conditions general use
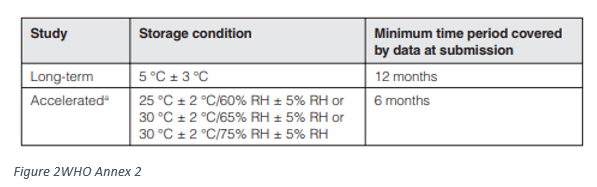
- Storage conditions: Active pharmaceutical ingredients intended for storage in a refrigerator
- Storage conditions: Active pharmaceutical ingredients intended for storage in a freezer

Attend the webinar 'Excursion Studies to Support Transporting and Distributing Clinical and Commercial Products' to take a deep dive into the effect of environmental factors during transportation and distribution and key factors to be considered to set up temperature-cycling studies to support excursions during shipping of pharmaceutical products depending on their label storage conditions.
The speaker, Kim Huynh-Ba, has almost 25 years of experience in analytical development, project management, strategic drug development and stability sciences. Kim has held several technical and quality positions at Astra Zeneca (formerly ICI Americas), DuPont Merck, DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb and Wyeth Vaccines.






